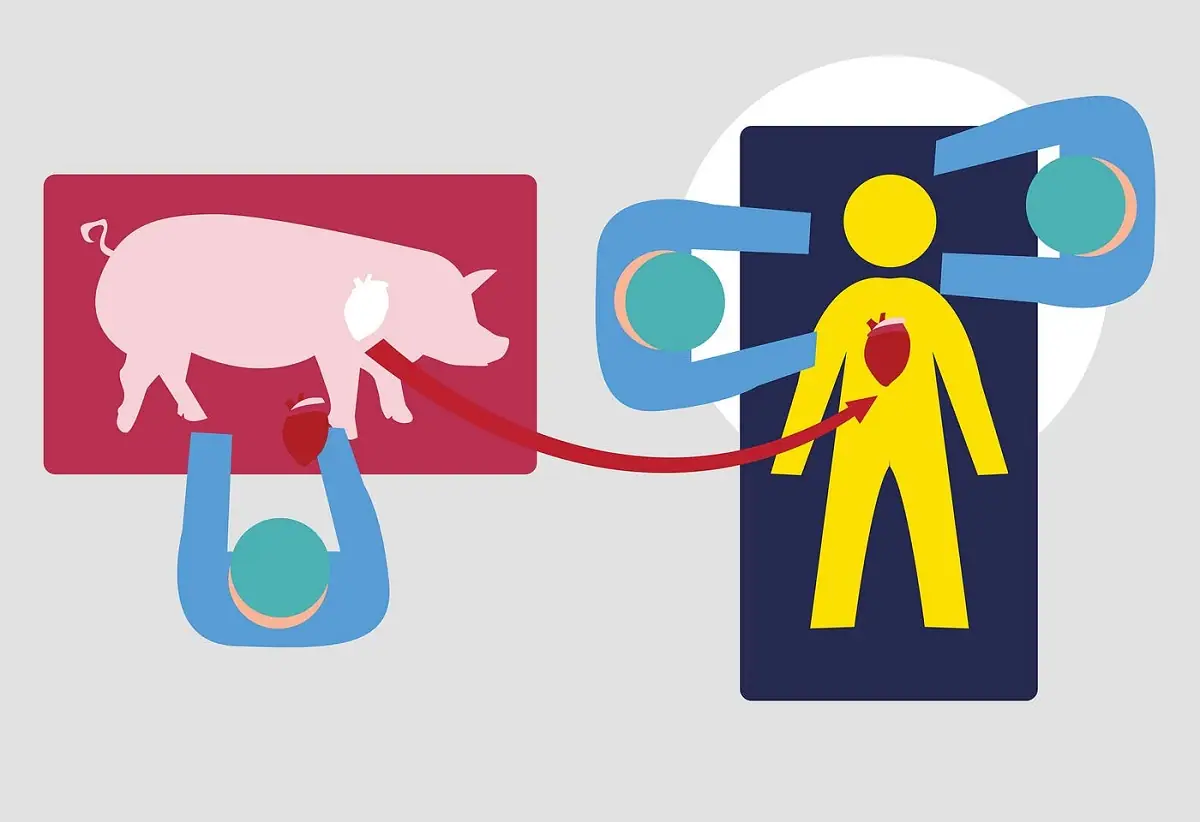
San Francisco, CA – Surgeons at the University of Maryland Medical Center (UMMC) have successfully transplanted a pig’s heart into a second patient, a 58-year-old man who was facing imminent death from heart disease. This is the second time in medical history that such a procedure has been performed, and it is a major breakthrough in the field of xenotransplantation, or the transplantation of organs from one species to another.
The patient, Lawrence Faucette, had been deemed ineligible for a traditional human heart transplant due to other health complications. However, he was approved for the experimental pig heart transplant under a special compassionate use authorization from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
The surgery was performed by Dr. Bartley P. Griffith, who also led the team that performed the world’s first pig heart transplant in January 2022. The surgery was a success, and Faucette is currently recovering well in the hospital.
“We are grateful to Lawrence for his willingness to participate in this groundbreaking trial,” said Dr. Griffith. “His bravery and selflessness will help to advance our knowledge of xenotransplantation and could potentially save the lives of many more people in the future.”
The successful pig heart transplant is a major step forward in the fight against heart disease, which is the leading cause of death in the United States. However, it is important to note that this is still an experimental procedure, and there are still many challenges that need to be addressed before xenotransplantation can be widely adopted.
Potential benefits of xenotransplantation
Xenotransplantation has the potential to revolutionize the field of organ transplantation. If successful, xenotransplantation could help to address the shortage of human donor organs and save the lives of many people who are currently waiting for transplants.
Challenges of xenotransplantation
One of the biggest challenges of xenotransplantation is the risk of organ rejection. When an organ is transplanted from one species to another, the recipient’s immune system is more likely to reject the organ. This is because the organ contains proteins that are foreign to the recipient’s body.
Another challenge of xenotransplantation is the risk of infection. Pigs can carry viruses and other pathogens that can be harmful to humans. Researchers are working on developing ways to reduce the risk of infection in xenotransplantation patients.
Future of xenotransplantation
Despite the challenges, researchers are optimistic about the future of xenotransplantation. The successful pig heart transplant is a major step forward, and it could pave the way for more widespread use of xenotransplantation in the future.

&w=360&resize=360,240&ssl=1)
&w=360&resize=360,240&ssl=1)
&w=360&resize=360,240&ssl=1)